Search Results for: primary cell wall
Primary cell wall
Definition noun plural: primary cell walls ˈpɹaɪməɹi sɛl wɔːl The layer of the plant cell wall that forms prior to... Read More
Secondary cell wall
Definition noun plural: secondary cell walls ˈsɛkənˌdɛɹi sɛl wɔːl The layer of the plant cell wall that forms... Read More
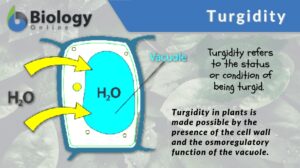
Turgor pressure
In biology, turgor pressure pertains to the pressure that is exerted by the fluid (e.g. water) against the cell wall. It is... Read More
Middle lamella
Definition noun plural: middle lamellae ˈmɪdəl ləˈmɛl.ə A pectin-rich intercellular material that glues the... Read More
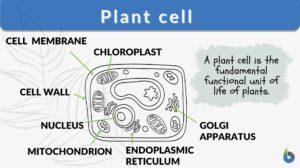
Plant cell
Plant Cell Definition A plant cell refers to any cell of a plant. It is the structural and functional unit of plants. Plant... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
Parenchyma
Parenchyma Definition What does parenchyma mean? Let's define the word "parenchyma". Most of the functional tissues in... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Primary meristem
Definition noun, plural: primary meristems (''botany') A type of meristem that is involved in the primary growth and thus... Read More
Collenchyma
Definition noun, plural: cholenchymas (botany) A fundamental type of tissue in plants characterized by cells with thicker... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Fluid mosaic model
Fluid Mosaic Model Definition What is the fluid mosaic model? The fluid mosaic model is a three-dimensional representation... Read More
Ground tissue
Definition noun, plural: ground tissues (botany) Any of the non-dermal, non-vascular tissue of vascular... Read More
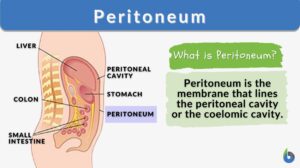
Peritoneum
What is the Peritoneum? The term peritoneum refers to the serous membrane that constitutes the biologically active inner... Read More
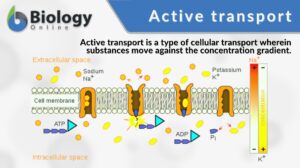
Active transport
Active transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances (e.g. ions, glucose, and amino acids) are transported... Read More
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Cells Definition What is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes,... Read More
Bast fiber
Definition noun (botany) The durable, nonliving sclerenchyma fiber in the phloem, providing support to the... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Hypertonic solution
Hypertonic Solution Definition Hypertonic solution is a relative term that describes the solution having a higher amount of... Read More
Sclerenchyma
Definition noun, plural: sclerenchymata, sclerenchymas (botany) A fundamental type of tissue in plants characterized by... Read More
Human Reproduction
Terminology and Concepts Primary reproductive organs are called gonads - testes in the male and ovaries in the female.... Read More
Golgi apparatus
Golgi Apparatus Definition The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role... Read More
Plant Tissues
Plants are composed of three major organ groups: roots, stems, and leaves. As we know from other areas of biology, these... Read More